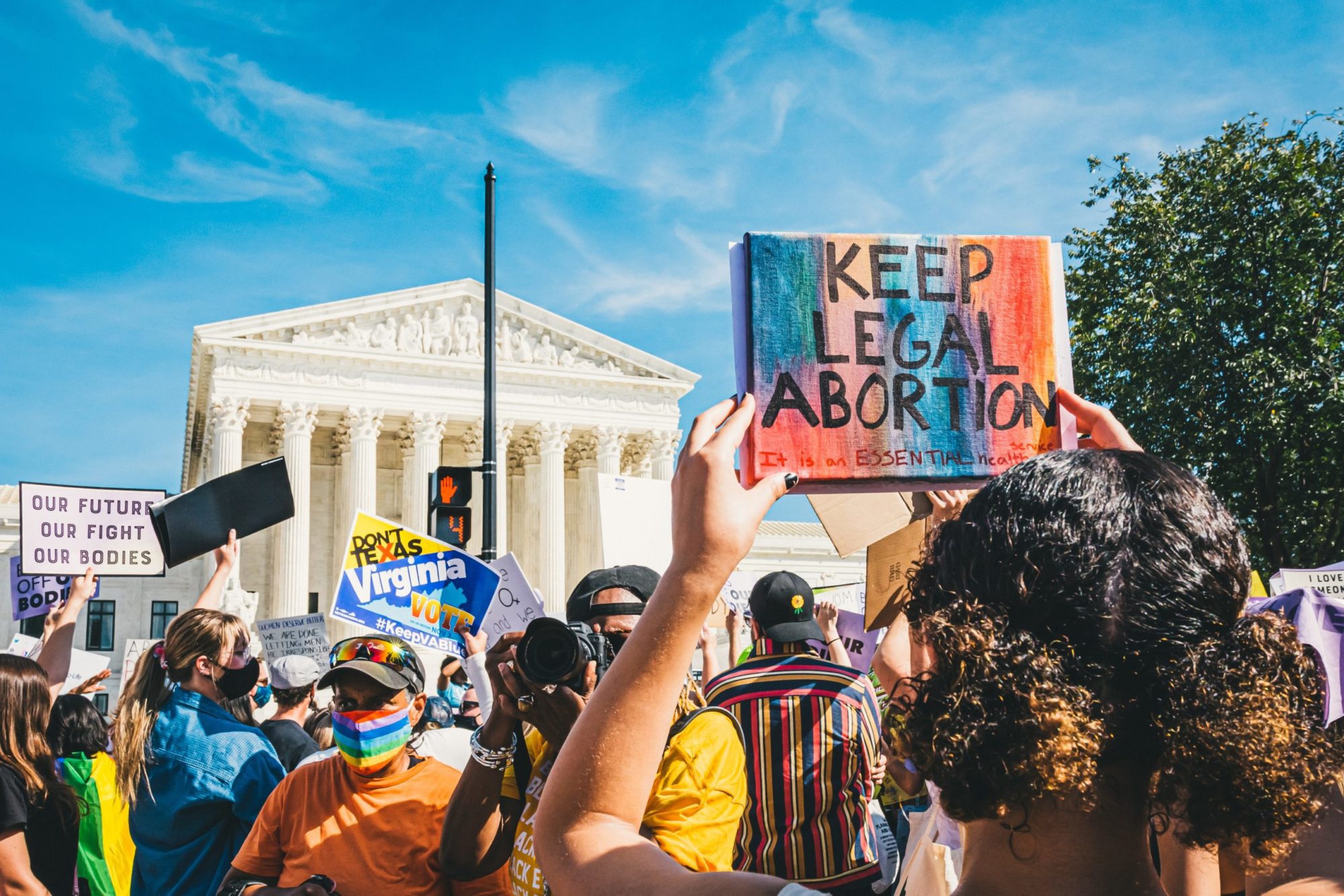
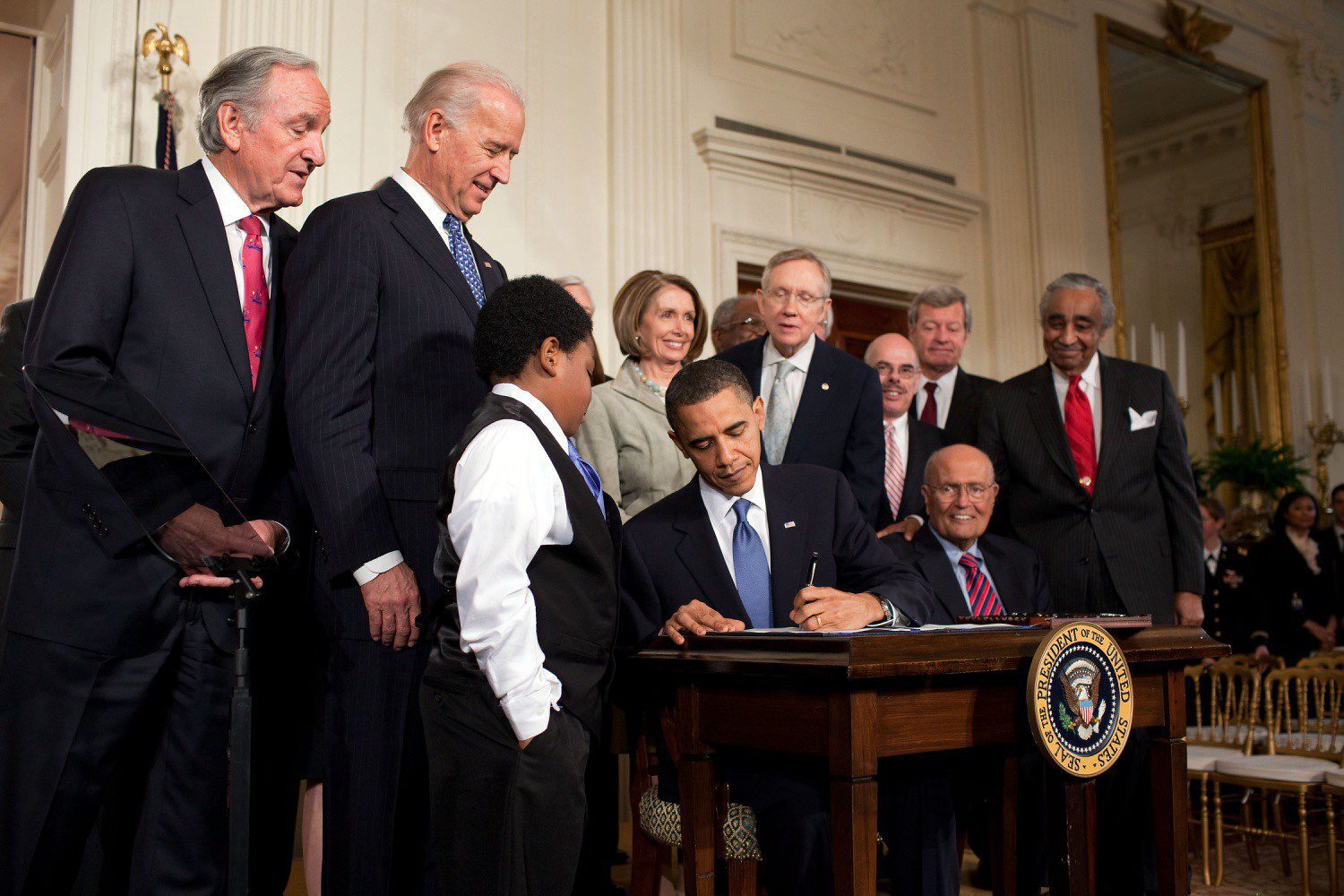
How Attacks Against Obamacare Turned Into Tools to Protect Abortion Access
Conservatives amended state constitutions to affirm broad rights for people to choose their health care. Now abortion rights proponents are taking them at their word.
Quinn Yeargain | March 3, 2023


Explore our ongoing Bolts series, Abortion Rights in State Constitutions.
A decade ago, when conservatives were attacking President Barack Obama’s Affordable Care Act as government encroachment in health care, they worked to amend state constitutions around the country to affirm a broad right for people to control their own medical decisions.
“Each competent adult shall have the right to make his or her own health care decisions,” reads section 38(a) of the Wyoming constitution’s Declaration of Rights, under the header “Right of healthcare access.” The provision was placed on Wyoming’s ballot by state lawmakers and approved by voters in 2012; voters saw ballot language that described the measure as preserving this right “from undue governmental infringement.”
Now these anti-ACA provisions—and their broad affirmations of a right to decide—have turned into an unlikely weapon in progressives’ fight against restrictions on abortion.
Reproductive rights advocates in Wyoming have sued to strike down the state’s abortion ban, saying that this “right to make . . . health care decisions” protects abortion access. A lawsuit in Ohio has made the same case using a similar provision in Ohio’s constitution that was adopted by voters in 2011.
“If you have an amendment that says you have the freedom to choose your health care, then that’s going to apply to all health care: that’s the argument being made,” says David Cohen, a professor of law at Drexel University who studies constitutions and abortion. “It’s like, ‘you used broad words, and these broad words have certain meanings, and we’re just applying those meanings to this context.’”
In both Ohio and Wyoming, these claims have seen early success in courts.
A trial court in Ohio issued a preliminary injunction against the state’s abortion restrictions in October. The judge found that the Health Care Freedom Amendment “bolsters the Ohio Constitution’s protection of liberty and personal autonomy and reinforces that these protections extend to Ohioans… the right to make decisions about their own bodies—including the fundamental right to make a decision as private and as central to a person’s bodily integrity as the decision to have an abortion.”
Freda Levenson, legal director of the ACLU of Ohio, which supports the lawsuit, says plainly, “The court was required to take this provision at its word: it preserves Ohioans’ freedom to choose their healthcare. And abortion is healthcare.”
In Wyoming, a trial court issued a preliminary injunction on a similar basis, concluding that it “could find that [section 38 of] the Wyoming Constitution affords all Wyoming citizens with a fundamental right to make their own health care decisions and that includes a Wyoming woman’s right to make her own decision regarding abortion.”
And provisions in several other state constitutions could be used for the same purpose.
Since the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Roe vs. Wade in June, legal organizations that are working to defend abortion rights have looked increasingly toward state courts and constitutions. This strategy’s most recent success came in January in South Carolina. Few states have constitutional language that explicitly protects abortion but many state courts have pointed to equal protection, due process, and privacy clauses to affirm a right to abortion under the state constitution, and strike down restrictions or bans on the procedure.
Plaintiffs are now adding last decade’s anti-ACA provisions to their repertoire. In Wyoming, plaintiffs cited ten different provisions of their state constitution, including section 38 but also Wyoming-specific protections of equality and the state’s equal-protection and due-process analogs. Similarly, in arguing in court that their state’s constitution contains “broad protections for individual liberties,” Ohio plaintiffs cited its equal protection and due process analogs, as well as the health care-freedom provision created in 2012.
“We see this as a very clear recognition by the voters of Ohio of the fundamental nature of the right to be free from government intrusion in private health care decisions,” Becca Kendis, one of the attorneys of record in the Ohio case and a Reproductive Rights Fellow at the Case Western Reserve School of Law, told Bolts about the state’s 2011 constitutional amendment.
The ACA’s passage in 2010 was not smooth. Polling during the congressional deliberations over its provisions indicated that it was very unpopular at the time, and the immediate response by Republican attorneys general and legislatures was to undermine its provisions. Throughout the country, conservatives championed constitutional amendments that established individual rights to health care, which built on Republican messaging that the ACA deprived Americans of their ability to choose their own doctors and make medical decisions. Most of these amendments were written narrowly. They referred specifically to an individual “right” to not participate in a specific health care system and not purchase health care or insurance, or to a right of patients to directly pay for health care services and of doctors to accept direct payments.
But the amendments also included expansive language that hinted at something broader. They articulated some sort of right that went beyond not participating in regulated health care markets.
The Alabama, Arizona, Florida, and Oklahoma amendments referred—in materially identical terms—to the “freedom” of their state residents “to provide for their [own] health care,” language that echoes Wyoming’s “right” to “make health care decisions.”
A measure in Colorado, which failed in 2010, even referred to a “right of health care choice.”
Reproductive rights proponents today are pointing to the breadth of that language to build their case that these clauses ought to apply to the right to choose an abortion.
For Kendis, the Ohio amendment’s drafters made a political choice to phrase their measure in vague and broad terms in order to maximize support for it.
“You can’t write it to get broad support and claim afterwards that it has this narrow application,” Kendis told Bolts. “If you’re writing something broadly because you’re trying to appeal to the broader public, what you write is what you get.” She added, “There’s a lot of thought process that goes into this to determine how to gain a majority of the vote.”
In both Ohio and Wyoming, appellate courts have declined to step in to block the trial courts’ injunctions, preventing the laws from coming into effect and allowing the lawsuits to continue in the trial courts.
Whether the Ohio and Wyoming supreme courts end up agreeing remains to be seen, though the new conservative majority in Ohio is likely uninterested in recognizing abortion rights. Still, these arguments have been cleverly framed to appeal to conservative jurists in both states.
A mainstay of the contemporary conservative legal movement is textualism, or the idea that a text should be interpreted based on its words’ meaning at the time of its adoption, judged by what a so-called ordinary speaker of the language would understand.
Kendis is framing her case as an easy one for such textualists. In 2011, she says, abortion was a “widely available, legal form of ‘health care’ by any plain meaning or definition of that word for four decades.”
The subjective intent of the amendment’s drafters may have been to push back against the ACA but “they could have very clearly worded this in a way that was targeting the ACA, the individual mandate,” she added. “They could’ve even defined ‘health care,’ so we really have to consider the plain meaning of the word in the text.” But that’s not what voters saw.
“At the end of the day, when the voters are going to read their ballots and they’re reading the language, they’re deciding whether they agree with the language,” she said. “I don’t see how anyone could argue that the voters, who approved this amendment, . . . were specifically excluding the right to abortion from the type of health care that they approved protection for.”
In two other states that adopted similar constitutional amendments last decade—Arizona and Oklahoma—abortion-rights activists are challenging the constitutionality of their state’s abortion restrictions. Litigants in neither case have cited their state constitutions’ similar health care freedom amendments—even though both are textually similar to Ohio’s. Alabama has a similar constitutional protection but voters ratified a constitutional amendment in 2018 establishing that “nothing in this constitution secures or protects a right to abortion.”
Whether litigants in Arizona or Oklahoma pursue similar arguments may depend on how the lawsuits play out in Ohio and Wyoming, though each state court system will be shaped by its own politics and members.
Still, the turnaround in these amendments’ use is a reminder of a history of unintended consequences for constitutional provisions that the right has used as well, for instance with the federal equal protections clause and affirmative action cases.
“It opens up a lot of possibilities once you look into what our constitution says, which we had not needed to rely on before Dobbs,” Kendis said.
Sign up and stay up-to-date
Our weekly newsletter on the local politics of criminal justice and voting rights